Osteogenesis imperfecta
Roots:
osteo– : of or relating to bone (Greek)
–genesis : formation, origination, creation (Greek)
im– (also in-, ir- and il-) : not, without (Latin)
Based on these roots, I can ascertain that this condition may have something to do with the improper formation of bones.
Osteogenesis imperfecta, also known as brittle bone disease, refers to a group of genetic disorders that result in fragile bones. The main cause is a congenital problem in the formation of type I collagen, which is vital to the formation of healthy bones. Patients with this condition can suffer from easily fractured bones, short stature, and hearing loss. Treatment options include surgical correction of bone deformities caused by repetitive fractures, fracture prevention, and drug therapy, including the use of growth hormones.
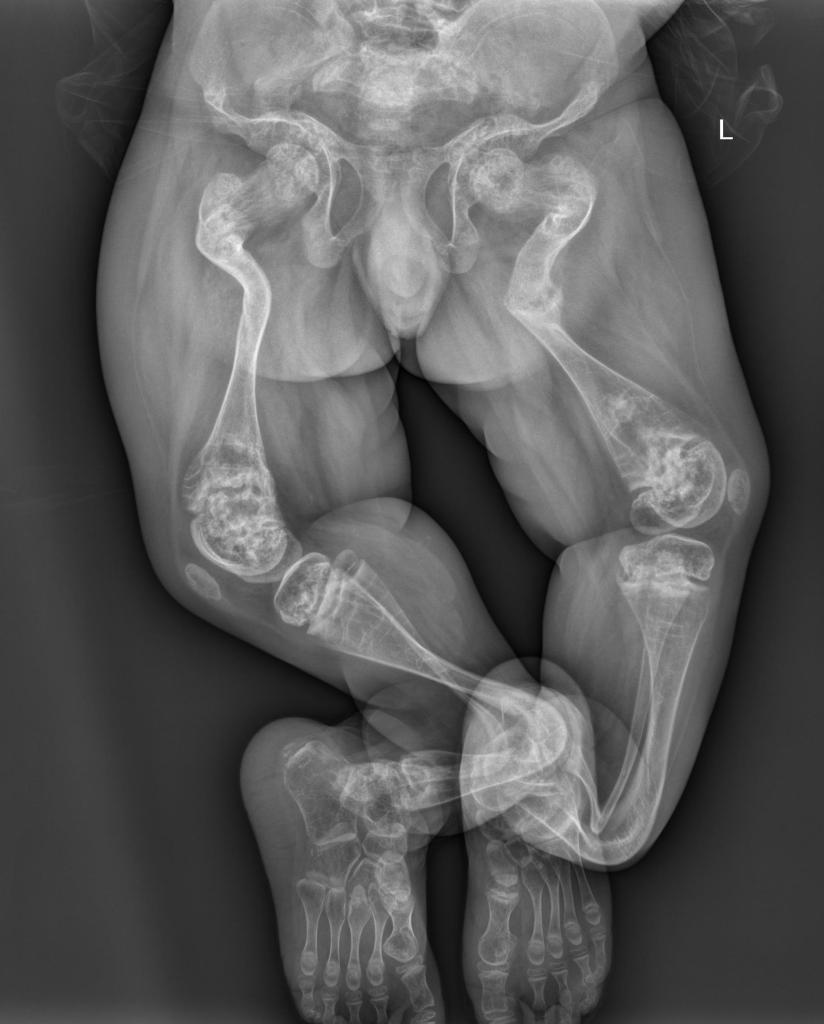
Image above shows the legs of a child affected by osteogenesis imperfecta – note the multiple fractures and malformed bones. Case courtesy of Badis Al Harbawi, Radiopaedia.org. From the case rID: 87221